The Age Reversal Blueprint!
Category: Healthy Aging

Ever wondered why two people of the same age can look so different? Chronologically, the two are the same age. Biologically, one is decades older.
Does one have secret expensive face creams? Good genes? What’s going on? Why are they aging in such different ways?
The answer is simple and it has to do with the activity in their cells.
- One is on a headlong path toward diseases and disorders.
- The other’s cells are renewing themselves and are living younger.
Why do people age at different rates?
Let’s dive into the complex yet fascinating world of aging, particularly, the groundbreaking Telomere Theory of Aging.
Aging isn’t just the number of candles on your birthday cake (your chronological age), it’s also about the health and vigor of your body’s systems, known as biological age.
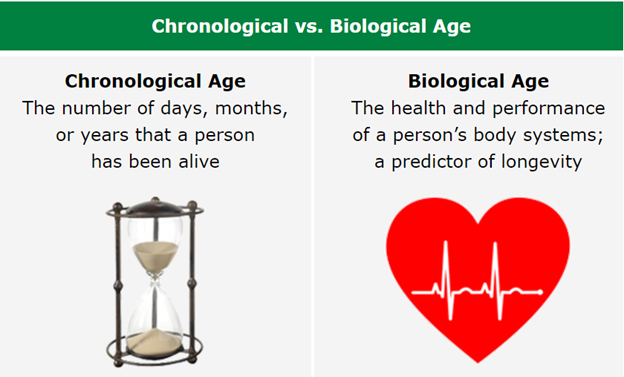
While chronological age marches on uniformly for everyone, biological age can vary widely between individuals. This distinction has spurred a new definition of anti-aging: the quest to slow, stop, or even reverse the biological aging process.
Jeanne Louise Calment (picured above) was a French supercentenarian and the oldest verified human, with a documented lifespan of 122 years and 164 days. How was she able to take up fencing at 85 when others are confined to wheelchairs and old folks’ homes?
How was Jeanne able to live so long?
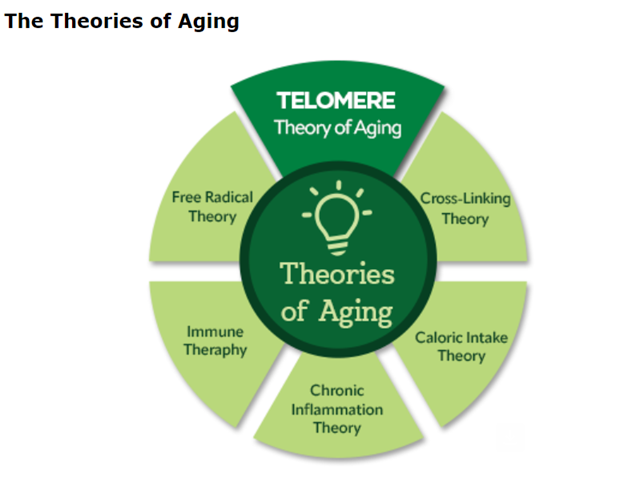
Among the various theories of aging, such as the Free-Radical and Cross-Linking theories, one has recently gained prominence due to its potential implications for health and longevity: the Telomere Theory of Aging.
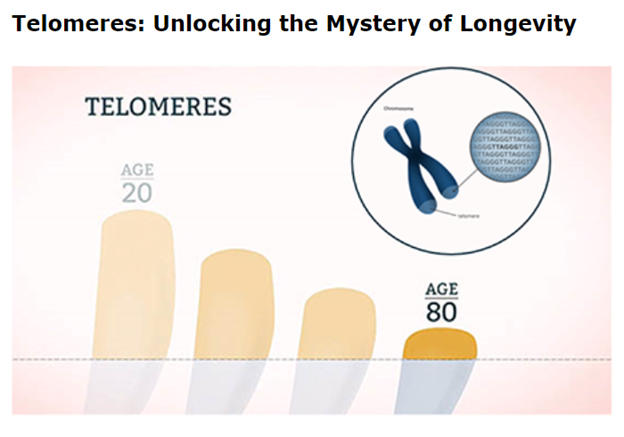
Picture this: at the ends of your chromosomes—those tiny structures carrying your genetic material—there are protective caps called telomeres.
They’re often compared to the plastic tips at the ends of shoelaces, keeping your DNA from “fraying.” However, each time a cell divides, these telomeres get shorter. Once telomeres are too short, cells age and can no longer divide, leading to the phenomena we associate with aging.
Here’s where it gets even more interesting.
The length of your telomeres could be a gauge of your biological age.
But can we influence our telomere length? Science says yes. Factors like nutrition, exercise, stress management, and sleep can actually slow down the rate of telomere shortening or, in some cases, lengthen them.
The implications of telomere science are profound.
By understanding and monitoring our telomeres, we can potentially make informed decisions to improve our health span, not just our lifespan.
Isn’t it fascinating to think that the secret to longevity might have been at our fingertips—or rather, at the tips of our chromosomes—all along?
Here are some of the benefits of longer telomeres:
- You remain healthier
- You look more vibrant
- Your eyes and skin will be brighter
- You’ll have more energy
- You’ll be more resistant to disease
If you’re as intrigued as I am, join our upcoming wellness webcast, The Age Reversal Blueprint with distinguished expert Dr. John Westerdahl, and discover groundbreaking insights into longevity, nutrition, and how you can turn back the clock on aging.
| Here’s to your health and longevity! |
Jerry Baker Wellness Guide 7036260774 |




Facebook Comments